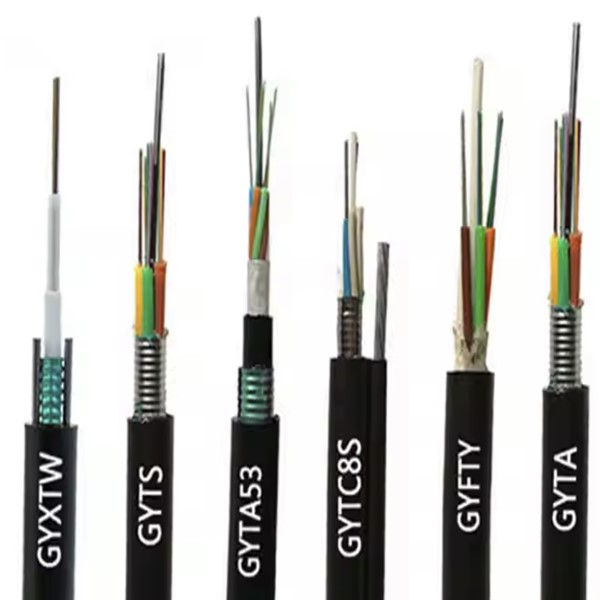
- Description
- Enquête
- Pièce jointe
Description
GYFTA53-14~18Xn Optic Cable is Stranded loose sleeve non-metallic reinforced core armored fiber optic cable
GYFTA53-14~18Xn Optic Cable Product Overview
GYFTA53 The structure of the fiber optic cable is that a 250μm optical fiber is sleeved into a loose tube made of high-modulus material, qui est rempli d'un composé imperméable. Au centre du noyau se trouve un noyau de renfort non métallique (PRF), et pour certains comptes de base, une couche de polyéthylène (PE) est pressé sur le noyau de renfort non métallique. Le tube lâche (et corde de remplissage) sont tordues autour d'un noyau de renforcement central pour former un noyau compact et rond, et les espaces à l'intérieur du noyau sont remplis d'un remplissage bloquant l'eau. La bande d'aluminium recouverte de plastique (APL) est pressé avec une couche de gaine intérieure en polyéthylène après un enveloppement longitudinal, et la bande d'acier plastifiée double face (PSP) is extruded with polyethylene outer sheath after longitudinal wrapping to form a cable.
A fiber optic cable is a communication line used for long-distance, high-speed data transmission, and its core component is an optical fiber made of high-purity glass or plastic. The optical cable uses the principle of total reflection of light to convert the electrical signal into an optical signal, transmit it through optical fiber, and then convert the optical signal back to the electrical signal at the receiving end, so as to realize the high-speed transmission of information.
GYFTA53-14~18Xn Optic Cable Product Pictures




GYFTA53-14~18Xn Optic Cable Product Specifications
| Fiber cable model (in increments of 2 fibres) | Number of optical fiber tubes | Number of sleeves | Number of filling ropes | Reference optical cable weight (kg/km) | Allowable tensile force Long-term/short-term (N) | Allowable crushing force long term/short term (N/100mm) | Bending radius static/dynamic (mm) | |
| GYFTA53-2~6Xn | 2~6 | 1 | 7 | 228 | 1000/3000 | 1000/3000 | 12.5J/25D | |
| GYFTA53-8~12Xn | 8~12 | 2 | 6 | 228 | ||||
| GYFTA53-14~18Xn | 14~18 | 3 | 5 | 228 | ||||
| GYFTA53-20~24Xn | 20~24 | 4 | 4 | 228 | ||||
| GYFTA53-26~30Xn | 26~30 | 5 | 3 | 228 | ||||
| GYFTA53-32~36Xn | 32~36 | 6 | 2 | 228 | ||||
| GYFTA53-38~42Xn | 38~42 | 7 | 1 | 228 | ||||
| GYFTA53-44~48Xn | 44~48 | 8 | 0 | 228 | ||||
| GYFTA53-50~60Xn | 50~60 | 5 | 3 | 240 | ||||
| GYFTA53-62~72Xn | 62~72 | 6 | 2 | 240 | ||||
| GYFTA53-74~84Xn | 74~84 | 7 | 1 | 240 | ||||
| GYFTA53-86~96Xn | 86~96 | 8 | 0 | 240 | ||||
| GYFTA53-98~108Xn | 98~108 | 9 | 1 | 276 | ||||
| GYFTA53-110~120Xn | 110~120 | 10 | 0 | 276 | ||||
| GYFTA53-122~132Xn | 122~132 | 11 | 1 | 326 | ||||
| GYFTA53-134~144Xn | 134~144 | 12 | 0 | 326 | ||||
| Fiber optic type | Atténuation (+ 20 ℃) | Bande passante | Ouverture numérique | Optical fiber cutoff wavelength | ||||
| @850nm | @1300nm | @1310nm | @1550nm | @850nm | @1300nm | |||
| G.652 | — | — | ≤0,36 dB/km | ≤0,22dB/km | — | — | — | ≤1260nm |
| G.655 | — | — | ≤0,40 dB/km | ≤0,23dB/km | — | — | — | ≤1450nm |
| 50/125µm | ≤3,3dB/km | ≤1,2dB/km | — | — | ≥500MHz·km | ≥500MHz·km | 0.200±0,015 s.o. | — |
| 62.5/125µm | ≤3,5dB/km | ≤1,2dB/km | — | — | ≥200MHz·km | ≥500MHz·km | 0.275±0,015 s.o. | — |
GYFTA53-14~18Xn Optic Cable Product Features
- Ultra-high bandwidth/extremely high capacity: The transmission bandwidth far exceeds that of copper cables (such as twisted pair and coaxial cables), and the theoretical transmission capacity of a single optical fiber can reach the Tbps level, which can easily meet the high-bandwidth requirements of high-definition video, Cloud computing, et 5G.
- Ultra-long transmission distance: Signal attenuation is minimal (especially in the 1550nm window), and the relay distance can reach tens or even hundreds of kilometers, which is much better than copper cables.
- Anti-electromagnetic interference: Optical fiber is an insulator, transmits optical signals, is completely unaffected by electromagnetic interference and lightning, and has obvious advantages in strong electromagnetic environments such as electric power and railways.
- Faible perte: Modern optical fibers have very low transmission losses (as low as 0.2dB/km).
- Petite taille et poids léger: Fiber optic cables are thinner and lighter than copper cables with the same transmission capacity, making them easy to lay and transport.
- Good confidentiality: Optical signals are transmitted inside the optical fiber and are not easy to be eavesdropped.
- No crosstalk: Fibers do not interfere with each other.
- Abundant resources: The main material is silica (sand), which comes from a wide range of sources.
GYFTA53-14~18Xn Optic Cable Product and More Optic Cables
Câble fibre optique non armé à tube central (GXY)
Câble à fibre optique blindé pour tube central (GYXS/GYXTW)
Câble à bande de fibres blindées légères toronnées à manchon lâche (GYDTS)
Câble à fibre optique non armé à gaine lâche et toronné (GYDTA)
Câble à fibre optique ignifuge non armé à noyau renforcé non métallique à gaine lâche toronné (GYFTZY)
Câble optique ignifuge blindé à noyau renforcé et toronné à manchon lâche(GYTZA53)
Câble à fibre optique blindé ignifuge à noyau renforcé non métallique à manchon lâche (GYFTZA53)
Câble à fibre optique ignifuge échoué (GYTZS)
Câble à fibre optique ignifuge non armé à gaine libre et toronné (GITZA)
Câble à fibre optique blindé simple à noyau de renforcement non métallique toronné (AG53)
Câble à fibre optique non armé à âme renforcée non métallique à gaine lâche et toronné (ENSEMBLE)
Câble optique à âme renforcée non métallique toronné à manchon lâche (GYHTY)
Câble à fibre optique non armé à âme renforcée non métallique à gaine lâche et toronné (LTD)
Câble optique blindé à fibre optique, fil d'acier rond mince simple échoué à manchon lâche (GYTA53 33)
GYFTA53-14~18Xn Optic Cable Product Applications
- Communication longue distance: Used for long-distance data transmission between countries and countries.
- Métro: Connects different network nodes within a city.
- Réseau local: Used for high-speed data transmission in local area networks such as businesses, écoles, and homes.
- Centre de données: Connecter les serveurs, stockage, and network equipment for high-speed internal communication.
GYFTA53-14~18Xn Optic Cable Product Structure

Désolé, aucune pièce jointe disponible !